Cloud computing is a beacon of transformational innovation in the ever-changing technological landscape. The growth of cloud computing has transformed how businesses deliver software, scale their operations, and interact across worldwide teams, from its humble beginnings with mainframe computers to the dynamic multi-cloud strategies of today. This essay digs into the tremendous impact of cloud technology, looking at how it has revolutionised software deployment, increased scalability, and enabled seamless remote communication. We reveal the limitless potential of cloud computing for businesses globally through an in-depth discussion of essential concepts, issues, and tactics. As we traverse the complex web of data protection, regulatory, and vendor concerns, it becomes clear that the cloud’s boundless future is primed to transform sectors and provide companies with unprecedented flexibility and resilience. Join us on an exploration of the heart of cloud technology, where innovation knows no bounds and possibilities are as limitless as the cloud itself.
Evolution of Cloud Computing
The Evolution of Cloud Computing contributes to a watershed moment in the history of information technology. It began with the dominance of Mainframe computers. Mainframe computers were the fundamental category of computing infrastructure in the early days of computing. These were big, centralised computers that several users could access remotely. With the advancement of technology, there was a shift toward distributed computing systems, in which numerous interconnected computers collaborated to complete complicated tasks.
The introduction of virtualization permitted the creation of virtual machines, which simulated numerous independent computer systems on a single physical machine. This boosted resource usage and flexibility significantly. The spread of high-speed internet and increased connectivity enabled distant access to these virtualized resources, giving rise to the concept of cloud services. The rise of the cloud continues to impact the current computing landscape, offering unprecedented scalability, flexibility, and accessibility for individuals and businesses alike.
Cloud computing can be separated into three general service delivery categories or forms of cloud computing. They are IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
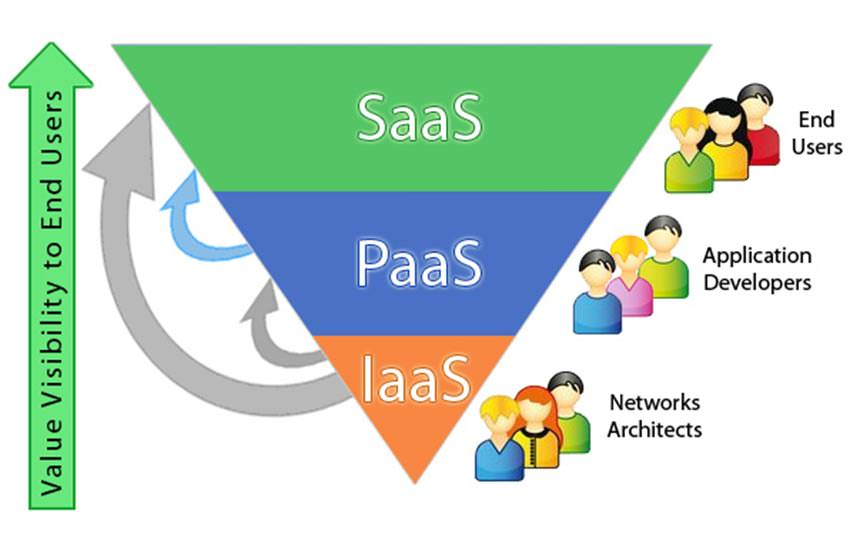
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS refers to a cloud service provider that is responsible for managing your infrastructure (the physical servers, network, virtualization, and data storage) over the Internet. The user gains access via an API or dashboard and, in essence, rents the infrastructure. The user manages things like the operating system, apps, and middleware, whereas the provider manages any hardware, networking, hard drives, data storage, and servers, as well as outages, repairs, and hardware concerns. This is the most common deployment model used by cloud storage providers.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS indicates that an outside cloud service provider offers and handles the hardware and an application-software platform, but the user manages the programs that run on top of the platform and the data on which the apps rely. PaaS provides customers with a shared cloud platform for application development and management (a crucial DevOps component) without the need to create and maintain the infrastructure typically involved with the process.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS is similar to renting a program over the Internet. Instead of being kept and handled on your computer, information is stored and managed by a firm on the Internet.SaaS programs are similar to websites and phone apps that may be accessed via a web browser. You must take care of things like software updates, bug fixes, and routine maintenance. You can access these cloud apps via a dashboard or an API. SaaS also eliminates the requirement for each individual user’s computer to have an app installed locally, allowing for more means of group or team access to the software.
Empowering Software Deployment
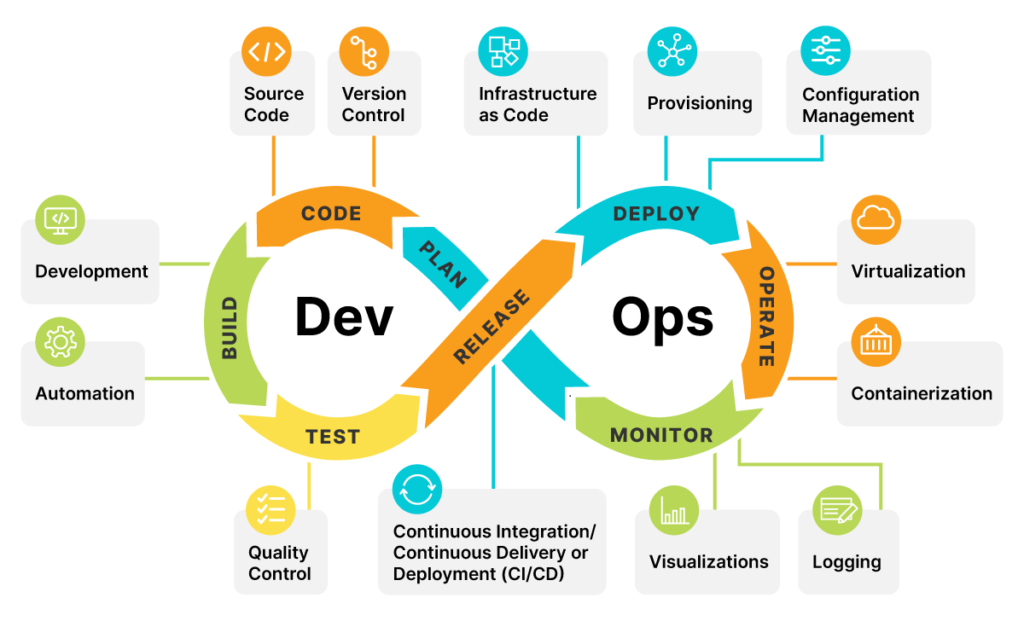
In cloud computing, rapid deployment cycles entail the efficient flow of software development from conception to deployment. Cloud-based solutions make this process easier by making resources for coding, testing, and deploying applications available. Cloud computing allows us to access software and services without being bound to individual computers. Incorporating new features and improvements is also made easier because there is no need to manually modify the real equipment.
DevOps and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) are contemporary methodologies for software development. Collaboration and automation between development and operations teams are emphasised in DevOps.This technique offers smooth software delivery by automating processes including code integration, testing, and deployment. By including automated testing to validate changes, automated deployment pipelines for prompt and reliable releases, and continuous integration of code changes, continuous integration and continuous delivery go one step further. The development process is streamlined, software quality is increased, and the deployment of new features and upgrades is accelerated thanks to this combination.
Scaling Horizons: Cloud’s Elasticity
Scalability is an important feature in cloud computing since it ensures that programs can handle variable levels of demand. Vertical scaling is the process of boosting the capacity of a single server by adding more RAM or CPU power to accommodate larger loads. Horizontal scaling, on the other hand, entails adding extra servers to divide the load, which in the long run can be more cost-effective and scalable. To maximise resource consumption, auto-scaling and load balancing work in tandem. Auto-scaling allows resources to be adjusted automatically based on demand, adding or deleting servers as needed. Load balancing evenly distributes incoming traffic across numerous servers to avoid overcrowding and ensure smooth operation.
The real-life advantage of cloud elasticity is revealed while dealing with traffic spikes and seasonal demand. Case studies of effective scaling implementations show how businesses managed abrupt surges in traffic while maintaining uninterrupted service. Furthermore, cloud systems provide cost efficiency through dynamic scaling, allowing firms to scale up during high demand and scale down during quieter periods. This not only improves performance but also reduces prices, making cloud computing a cost-effective choice for enterprises of all sizes.
Facilitating Global Teams
Virtual workspaces and cloud-based collaboration tools have transformed the facilitation of global teams. These technologies enable teams spread across multiple locations to collaborate in real-time, allowing for seamless communication and project collaboration. Geographical borders become meaningless when using the power of the cloud, and team members can collaborate as if they were in the same physical space. This level of communication not only boosts productivity but also develops a sense of oneness among members of the global team.
In the cloud computing ecosystem, enhanced security and compliance are critical issues. Secure cloud infrastructures use strong measures like encryption, authentication procedures, and stringent access restrictions to safeguard sensitive data and prevent illegal access. Cloud providers adhere to various rules, including GDPR and HIPAA, to ensure legal data handling and storage practices, providing businesses with peace of mind that their data is maintained with the highest levels of security and compliance.
Multi-Cloud Strategies: Diversifying Possibilities
Multi-Cloud Strategies provide firms with a varied approach to cloud computing, with a variety of advantages and prospects.
Disaster recovery and redundancy are essential components of multi-cloud solutions. Businesses can maintain continued operations even in the face of unexpected outages or calamities affecting a single cloud provider by leveraging numerous cloud providers. This redundancy improves business continuity while lowering the risks associated with relying primarily on one cloud platform. It essentially serves as an insurance policy against unforeseeable disruptions.
Using the Best-of-the-BestBreed Services enables enterprises to leverage the distinct strengths and specialised offers of many cloud providers. Each provider excels in different areas, such as sophisticated analytics, machine learning, or industry-specific solutions. Businesses can construct a customised infrastructure that matches their individual demands and obtains a competitive edge in their market by carefully mixing these services from several clouds. This method enables businesses to enhance their operations by employing the greatest resources available across several cloud platforms.
Challenges and Considerations
In a multi-cloud context, data privacy and compliance pose substantial issues. It might be difficult to manage data residency and compliance needs across various cloud providers. To guarantee that sensitive information is handled and used in accordance with applicable regulations, organisations must carefully negotiate legal and regulatory landscapes. Implementing strong data encryption and privacy protection mechanisms is critical for preserving data integrity and keeping it confidential and secure.
In a multi-cloud approach, vendor lock-in and interoperability are essential issues. Dependence on a single cloud provider can lead to vendor lock-in, making switching costly. Companies should consider vendor-specific services and create interoperability standards to reduce risk. Using multiple cloud platforms allows seamless app and data operation, allowing businesses to update their infrastructure without reliance on a single provider.
Cloud computing is revolutionising business technology and communication by enabling rapid deployment cycles and DevOps approaches, enabling businesses to market their applications more effectively and efficiently than ever before. This agility is enhanced by the cloud’s elasticity, which allows resources to increase easily in response to demand spikes.
Furthermore, the capacity to assist global teams via virtual workplaces and collaboration tools overcomes geographical barriers, allowing various teams to operate harmoniously together. This not only broadens the talent pool but also stimulates creativity by bringing together a diverse set of viewpoints and experiences.
Multi-cloud solutions are an example of foresight, providing redundancy, disaster recovery, and access to specialized services from several cloud providers. This diversity in cloud adoption not only ensures business continuity but also helps enterprises capitalize on the distinct qualities of various platforms, creating a competitive advantage.

